How to use Chroma DB step-by-step guide

Vector databases have seen an increase in popularity due to the rise of Generative AI and Large Language Models (LLMs). Vector databases can be used in tandem with LLMs for Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) - i.e. a framework for improving the quality of LLM responses by grounding prompts with context from external systems.
What is Chroma DB?
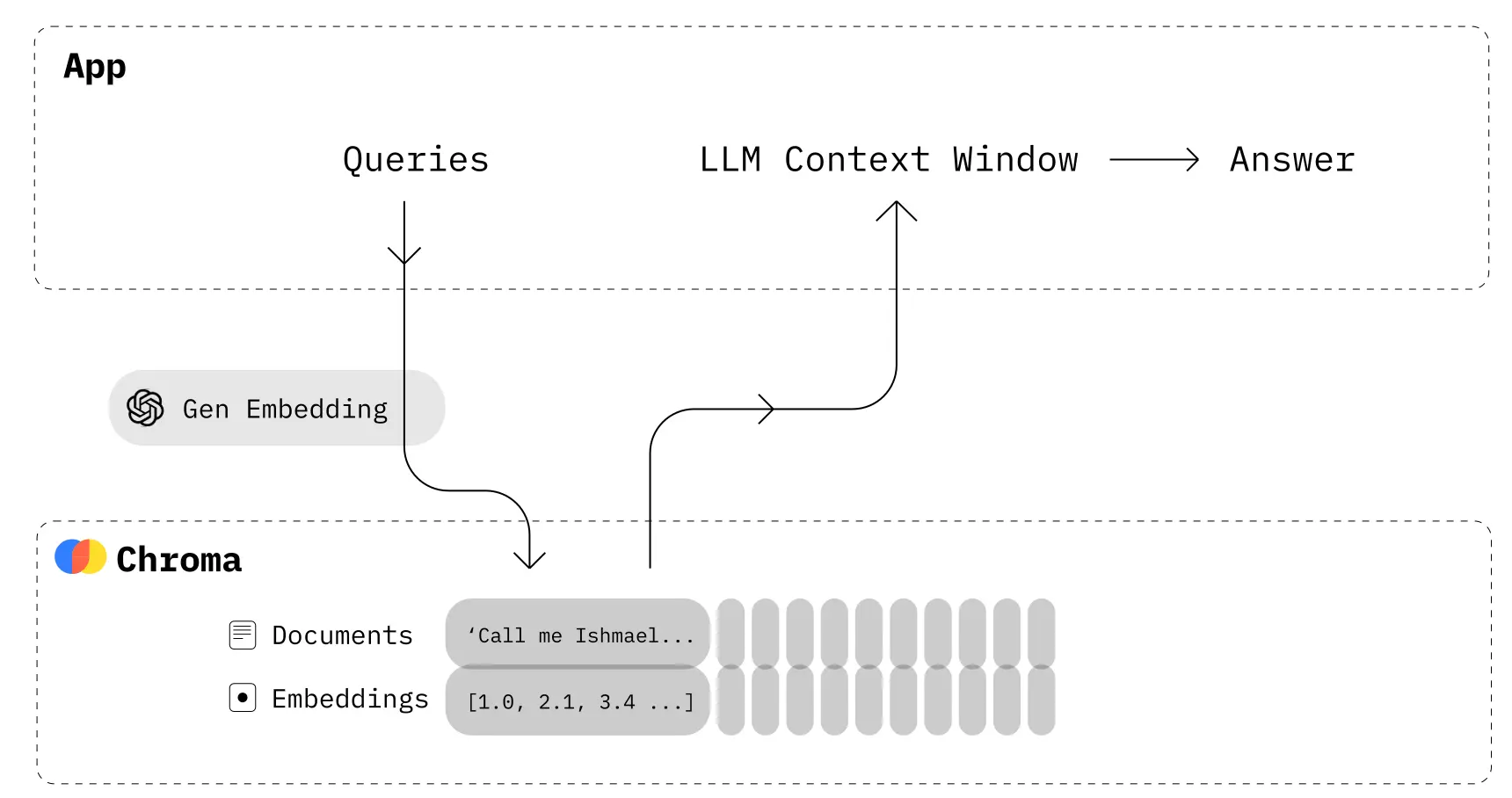
Chroma is an open-source embedding database that enables retrieving relevant information for LLM prompting. It emphasizes developer productivity, speed, and ease-of-use.
Chroma provides several great features:
- Use in-memory mode for quick POC and querying.
- Reuse collections between runs with persistent memory options.
- Add and delete documents after collection creation.
- Query based on document metadata & page content.
Installing Chroma DB
To install Chroma DB for Python, simply run the following pip command:
1pip install chromadbCreating a vector database using Chroma DB
Chroma organizes data using a collection primitive type to manage collections of embeddings.
Create a collection using default embedding function
1import chromadb
2
3client = chromadb.Client()
4client.create_collection(name="collection_name")Create a collection using specific embedding function
Chroma uses the all-MiniLM-L6-v2 model for creating embeddings. When instantiating a collection, we can provide the embedding function. Here, we’ll use the default function for simplicity.
1import chromadb
2from chromadb.utils import embedding_functions
3
4ef = embedding_functions.DefaultEmbeddingFunction()
5client = chromadb.Client()
6client.create_collection(name="collection_name", embedding_function=ef)Chroma offers integrations with vendors such as OpenAI, Hugging Face, Cohere and more.
Writing a custom embed function is also supported:
1from chromadb import Documents, EmbeddingFunction, Embeddings
2
3class MyEmbeddingFunction(EmbeddingFunction):
4 def __call__(self, texts: Documents) -> Embeddings:
5 # embed the documents somehow
6 return embeddingsUsing collections in Chroma DB
In this section, we explore useful techniques for managing and using collections in Chroma DB.
Delete collections
1import chromadb
2
3client = chromadb.Client()
4client.create_collection(name="collection_name")
5client.delete_collection(name="collection_name")Get existing collection
1import chromadb
2
3client = chromadb.Client()
4client.create_collection(name="collection_name")
5collection = client.get_collection(name="collection_name")Get or create collection
Chroma provides a convenient method for either getting an existing collection or creating a new one:
1import chromadb
2
3client = chromadb.Client()
4collection = client.get_or_create_collection(name="collection_name")Adding data to collections
Adding data to a collection is straightforward with Chroma’s API. When you pass a list of documents to Chroma, it automatically tokenizes, embeds, and stores them.
1import chromadb
2
3client = chromadb.Client()
4collection = client.get_or_create_collection(name="collection_name")
5collection.add(
6 documents=["document1", "document2", "document3"],
7 metadatas=[{"type": "recipe"}, {"type": "article"}, {"type": "article"}],
8 ids=["1", "2", "3"]
9)- The
documentsfield provides the raw text for automatic conversion using the embedding function metadatasis an optional field corresponding to the uploaded documents. It’s optional but recommended for later querying.idsis a required field for the documents. The order is important as it matches the document sequence.
Querying data in a collection
1import chromadb
2
3client = chromadb.Client()
4collection = client.get_or_create_collection(name="collection_name")
5collection.add(
6 documents=["document1", "document2", "document3"],
7 metadatas=[{"type": "recipe"}, {"type": "article"}, {"type": "article"}],
8 ids=["1", "2", "3"]
9)
10
11results = collection.query(
12 query_texts=["document"],
13 n_results=2,
14 where={"type": "article"}
15)
16
17print(results)Output:
1{
2 'ids': [['2', '3']],
3 'distances': [
4 [0.5050200819969177, 0.5763288140296936]
5 ],
6 'metadatas': [
7 [{'type': 'article'}, {'type': 'article'}]
8 ],
9 'embeddings': None,
10 'documents': [
11 ['document2', 'document3']
12 ],
13 'uris': None,
14 'data': None
15}- The
query_textsfield provides the raw query string, which is automatically processed using the embedding function. n_resultsspecifies the number of results to retrieve.- The
whereclause enables metadata-based filtering.
In addition, the where field supports various operators:
1import chromadb
2
3client = chromadb.Client()
4collection = client.get_or_create_collection(name="collection_name")
5collection.add(
6 documents=["document1", "document2", "document3"],
7 metadatas=[{"type": "recipe"}, {"type": "article"}, {"type": "article"}],
8 ids=["1", "2", "3"]
9)
10
11results = collection.query(
12 query_texts=["document"],
13 n_results=2,
14 where={
15 "type": {
16 "$eq": "article"
17 }
18 }
19)For the list of supported operators, refer to the documentation here.
Filtering based on document content is also possible:
1import chromadb
2
3client = chromadb.Client()
4collection = client.get_or_create_collection(name="collection_name")
5collection.add(
6 documents=["document1", "document2", "document3"],
7 metadatas=[{"type": "recipe"}, {"type": "article"}, {"type": "article"}],
8 ids=["1", "2", "3"]
9)
10
11results = collection.query(
12 query_texts=["document"],
13 n_results=2,
14 where={"type": "article"},
15 where_document={"$contains": "2"}
16)
17
18print(results)Output:
1{
2 'ids': [['2']],
3 'distances': [[0.5050200819969177]],
4 'metadatas': [[{'type': 'article'}]],
5 'embeddings': None,
6 'documents': [['document2']],
7 'uris': None,
8 'data': None
9}Getting documents based on id in the collection
Retrieve specific documents by their IDs using the collection.get method:
1import chromadb
2
3client = chromadb.Client()
4collection = client.get_or_create_collection(name="collection_name")
5collection.add(
6 documents=["document1", "document2", "document3"],
7 metadatas=[{"type": "recipe"}, {"type": "article"}, {"type": "article"}],
8 ids=["1", "2", "3"]
9)
10
11results = collection.get(
12 ids=["1"]
13)
14
15print(results)Output:
1{
2 'ids': ['1'],
3 'embeddings': None,
4 'metadatas': [{'type': 'recipe'}],
5 'documents': ['document1'],
6 'uris': None,
7 'data': None
8}where and where_document filters may also be used. If ids are not provided, all items matching the where and where_document conditions will be returned.
Getting all documents in the collection
Retrieve all documents in a collection:
1import chromadb
2
3client = chromadb.Client()
4collection = client.get_or_create_collection(name="collection_name")
5collection.add(
6 documents=["document1", "document2", "document3"],
7 metadatas=[{"type": "recipe"}, {"type": "article"}, {"type": "article"}],
8 ids=["1", "2", "3"]
9)
10
11results = collection.get()
12print(results)Output:
1{
2 'ids': ['1', '2', '3'],
3 'embeddings': None,
4 'metadatas': [
5 {'type': 'recipe'},
6 {'type': 'article'},
7 {'type': 'article'}
8 ],
9 'documents': ['document1', 'document2', 'document3'],
10 'uris': None,
11 'data': None
12}Updating documents in a collection
Update existing documents in a collection with new embeddings or data using the collection.update method.
1import chromadb
2
3client = chromadb.Client()
4collection = client.get_or_create_collection(name="collection_name")
5collection.add(
6 documents=["document1", "document2", "document3"],
7 metadatas=[{"type": "recipe"}, {"type": "article"}, {"type": "article"}],
8 ids=["1", "2", "3"]
9)
10collection.update(
11 documents=["document10"],
12 metadatas=[{"type": "article"}],
13 ids=["1"]
14)
15
16results = collection.get(
17 ids=["1"]
18)
19print(results)Output:
1{
2 'ids': ['1'],
3 'embeddings': None,
4 'metadatas': [{'type': 'article'}],
5 'documents': ['document10'],
6 'uris': None,
7 'data': None
8}if a provided id is not found, an error is logged and the update is ignored.
Chroma also supports the collection.upsert operation as well:
1import chromadb
2
3client = chromadb.Client()
4collection = client.get_or_create_collection(name="collection_name")
5collection.upsert(
6 documents=["document1", "document2", "document3"],
7 metadatas=[{"type": "recipe"}, {"type": "article"}, {"type": "article"}],
8 ids=["1", "2", "3"]
9)Deleting documents in a collection
Documents can be deleted from a collection using the collection.delete method:
1import chromadb
2
3client = chromadb.Client()
4collection = client.get_or_create_collection(name="collection_name")
5collection.upsert(
6 documents=["document1", "document2", "document3"],
7 metadatas=[{"type": "recipe"}, {"type": "article"}, {"type": "article"}],
8 ids=["1", "2", "3"]
9)
10
11collection.delete(ids=["1"])
12print(collection.count())Output:
12Similarly to the collection.get, an optional where filter may be supplied. If no ids are supplied, it deletes all the documents that match the where conditions.
Counting the number of documents in a collection
1import chromadb
2
3client = chromadb.Client()
4collection = client.get_or_create_collection(name="collection_name")
5collection.upsert(
6 documents=["document1", "document2", "document3"],
7 metadatas=[{"type": "recipe"}, {"type": "article"}, {"type": "article"}],
8 ids=["1", "2", "3"]
9)
10
11print(collection.count())Output:
13Modifying an existing collection
Collection names may be modified after creation:
1import chromadb
2
3client = chromadb.Client()
4collection = client.get_or_create_collection(name="collection_name")
5collection.modify(name="new_collection_name")Listing all collections in a client
1import chromadb
2
3client = chromadb.Client()
4client.get_or_create_collection(name="collection_one")
5client.get_or_create_collection(name="collection_two")
6print(client.list_collections())Output:
1[Collection(name=collection_two), Collection(name=collection_one)]Persisting vector databases using Chroma DB
The in-memory Chroma client provides saving and loading to disk functionality with the PersistentClient.
Saving to disk
1import chromadb
2
3client = chromadb.PersistentClient(path="document_store")
4collection = client.get_or_create_collection(name="collection_name")
5collection.upsert(
6 documents=["document1", "document2", "document3"],
7 metadatas=[{"type": "recipe"}, {"type": "article"}, {"type": "article"}],
8 ids=["1", "2", "3"]
9)Loading an existing from disk
1import chromadb
2
3client = chromadb.PersistentClient(path="document_store")
4collection = client.get_or_create_collection(name="collection_name")
5#collection.upsert(
6# documents=["document1", "document2", "document3"],
7# metadatas=[{"type": "recipe"}, {"type": "article"}, {"type": "article"}],
8# ids=["1", "2", "3"]
9#)
10print(collection.get())Output:
{
'ids': ['1', '2', '3'],
'embeddings': None,
'metadatas': [
{'type': 'recipe'},
{'type': 'article'},
{'type': 'article'}
],
'documents': ['document1', 'document2', 'document3'],
'uris': None,
'data': None
}Running Chroma DB as a server
Chroma may be used as a standalone server. Simply run the following command:
1chroma run --path /document_storeOutput:
1
2
3 ((((((((( (((((####
4 ((((((((((((((((((((((#########
5 ((((((((((((((((((((((((###########
6 ((((((((((((((((((((((((((############
7 (((((((((((((((((((((((((((#############
8 (((((((((((((((((((((((((((#############
9 (((((((((((((((((((((((((##############
10 ((((((((((((((((((((((((##############
11 (((((((((((((((((((((#############
12 ((((((((((((((((##############
13 ((((((((( #########
14
15
16
17Running Chroma
18
19Saving data to: document_store
20Connect to chroma at: http://localhost:8000
21Getting started guide: https://docs.trychroma.com/getting-startedThen connect to the local host using the HttpClient:
1import chromadb
2
3client = chromadb.HttpClient(host="localhost", port=8000)
4print(client.list_collections())Output:
1[Collection(name=collection_name)]